Information Elements¶
Introduction¶
The information elements (also IM elements, elements of information metabolism, or, confusingly, “functions”) are eight mental categories that play a key role in interpersonal interaction. They are denoted using the same symbols and names as the information aspects. The difference between them is that information elements are subjective properties of the psyche, whereas information aspects are objective properties of reality independent from psyche.
Information Element Notations¶
Name |
Symbol |
2-letter |
1-letter |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Si |
S |
|
|
Ne |
I |
|
|
Ti |
L |
|
|
Fe |
E |
|
|
Ni |
T |
|
|
Se |
F |
|
|
Fi |
R |
|
|
Te |
P |
Information Element Themes¶
Si 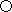 Introverted Sensing: homeostasis, continuity, smoothness, flow, satisfaction, aesthetics, quality of life, pleasure, relaxation, convenience, quality
Introverted Sensing: homeostasis, continuity, smoothness, flow, satisfaction, aesthetics, quality of life, pleasure, relaxation, convenience, quality
Ne  Extraverted Intuition: potential, permutation, isomorphism, semblance, essence, uncertainty, the unknown, opening up new “windows” and bringing up new possibilities in conversation, seeing opportunities, chance, being the first, refreshing informational suddenness, diversity of interests and involvements
Extraverted Intuition: potential, permutation, isomorphism, semblance, essence, uncertainty, the unknown, opening up new “windows” and bringing up new possibilities in conversation, seeing opportunities, chance, being the first, refreshing informational suddenness, diversity of interests and involvements
Ti 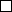 Introverted Logic: structure, analysis, coherence, consistency, cogency, accordance, match, commensurability, understanding, order, or the lack of thereof
Introverted Logic: structure, analysis, coherence, consistency, cogency, accordance, match, commensurability, understanding, order, or the lack of thereof
Fe  Extraverted Ethics: emotional atmosphere, romanticism, cooperation, treatment, qualitative judgement of behavior, sympathy, ethical estimations of observable actions, “ethics of actions”
Extraverted Ethics: emotional atmosphere, romanticism, cooperation, treatment, qualitative judgement of behavior, sympathy, ethical estimations of observable actions, “ethics of actions”
Ni 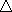 Introverted Intuition: development over time, historicity, cause and effect, consequences, repetition, archetypal themes and examples, looking for causes in history or the past, past-future forecasting of event dynamics, rhythm, delay or act-now, past-turned imagination
Introverted Intuition: development over time, historicity, cause and effect, consequences, repetition, archetypal themes and examples, looking for causes in history or the past, past-future forecasting of event dynamics, rhythm, delay or act-now, past-turned imagination
Se  Extraverted Sensing: sensing of immediate static qualities of objects, sensing of immediate reality, external appearance, texture, form, static objects, impact, direct physical effect, span, extent, scope
Extraverted Sensing: sensing of immediate static qualities of objects, sensing of immediate reality, external appearance, texture, form, static objects, impact, direct physical effect, span, extent, scope
Fi 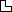 Introverted Ethics: internal harmony, resonance or dissonance of personal sentiments, sympathy, pity, compassion, support, condemnation, judgement, positive and negative emotional space
Introverted Ethics: internal harmony, resonance or dissonance of personal sentiments, sympathy, pity, compassion, support, condemnation, judgement, positive and negative emotional space
Te  Extraverted Logic: efficiency, method, mechanism, knowledge, work, reason in motion, direction of activity into its most logical course of action, “logic of actions”, utilitarianism, expediency, benefit
Extraverted Logic: efficiency, method, mechanism, knowledge, work, reason in motion, direction of activity into its most logical course of action, “logic of actions”, utilitarianism, expediency, benefit
States of Mind¶
When a person is “using” an element he naturally goes into a corresponding state of mind, which is reflected in his body language and vocabulary, and tends to have a similar effect on the people around him, who will react based on which function that element occupies in their Model A, with interest (Ego), amusement (Super-Id), boredom (Id), or irritation (Super-Ego), etc.
Si
 : a physically relaxed state of mind, turned to the continuity and flow of the moment
: a physically relaxed state of mind, turned to the continuity and flow of the momentNe
 : seeing the potential on the current situation, bringing up various possibilities up to discussion, recombinative play, permutations, variations, alternatives, solutions, including options that seem improbable or even absurd at times, informationally renovative and refreshing conversation
: seeing the potential on the current situation, bringing up various possibilities up to discussion, recombinative play, permutations, variations, alternatives, solutions, including options that seem improbable or even absurd at times, informationally renovative and refreshing conversationTi
 : analytical state of mind, clarity and exactitude of thought, a sense of coherence, order, and regularity at different levels of structure, “debugging”: seeing the whole system and then spotting nonsensical flaws or mistakes, or alternatively building one’s own systems from simple and well-understood parts
: analytical state of mind, clarity and exactitude of thought, a sense of coherence, order, and regularity at different levels of structure, “debugging”: seeing the whole system and then spotting nonsensical flaws or mistakes, or alternatively building one’s own systems from simple and well-understood partsFe
 : assessing the moods and attitudes from dynamics of surroundings and the actions and choices of others, being perceptive of the “emotional atmosphere”, analyzing and evaluating emotions and attitudes of others based on their currently observable reactions and actions, with to express one’s feelings and experiences openly and directly, to impact the emotional and social space, which can be done through expressive combination of words and gestures
: assessing the moods and attitudes from dynamics of surroundings and the actions and choices of others, being perceptive of the “emotional atmosphere”, analyzing and evaluating emotions and attitudes of others based on their currently observable reactions and actions, with to express one’s feelings and experiences openly and directly, to impact the emotional and social space, which can be done through expressive combination of words and gesturesNi
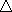 : a protracted and reflective state of mind, “falling out of time” and later trying to make up for lost activity, generalizing and abstracting past events from memory, using these generalizations to see what’s going to happen, reflecting upon the past in order to be able to evaluate what is possible to do in the present moment and to predict the most likely course of events, patience that borders with inactivity
: a protracted and reflective state of mind, “falling out of time” and later trying to make up for lost activity, generalizing and abstracting past events from memory, using these generalizations to see what’s going to happen, reflecting upon the past in order to be able to evaluate what is possible to do in the present moment and to predict the most likely course of events, patience that borders with inactivitySe
 : awareness of the space and concrete environment around oneself, externally observatory state of mind, “sensing of reality”, “factual perception of reality”, everything around you gets registered no matter if you can touch it or it’s way off in the distant distance, a mobilized state, exerting force on objects and people with the goal of moving them around in space, in Se perception a person or object can be influenced only in space
: awareness of the space and concrete environment around oneself, externally observatory state of mind, “sensing of reality”, “factual perception of reality”, everything around you gets registered no matter if you can touch it or it’s way off in the distant distance, a mobilized state, exerting force on objects and people with the goal of moving them around in space, in Se perception a person or object can be influenced only in spaceFi
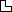 : an analytical state of mind, analysis of personal feeling and stances, harmony or disharmony of personal values and sentiments, endearment, closeness, moral satisfaction, emotional sensitivity, deep personal conviction that may produce moral firmness and resolve
: an analytical state of mind, analysis of personal feeling and stances, harmony or disharmony of personal values and sentiments, endearment, closeness, moral satisfaction, emotional sensitivity, deep personal conviction that may produce moral firmness and resolveTe
 : an evaluatory state of mind that directly assesses events and actions of other people from logical POV and openly voices those assessments, assessing and estimating productivity, efficiency, usefulness, rational sense of any given involvement venture or activity, steady and purposeful state of mind that leads to making rational actions despite the present sentiments
: an evaluatory state of mind that directly assesses events and actions of other people from logical POV and openly voices those assessments, assessing and estimating productivity, efficiency, usefulness, rational sense of any given involvement venture or activity, steady and purposeful state of mind that leads to making rational actions despite the present sentiments
Information Element Dichotomies¶
Warning
This page or section is incomplete. Additional contributions are needed.
There are 3 basic dichotomies of information aspects, and thus 4 derived dichotomies (see the mathematics of the Reinin dichotomies.)
The dichotomies Static / Dynamic and Extroverted / Introverted (a.k.a. Body / Field) came from Aushra Augusta, and External / Internal was suggested by another early author. However, this last dichotomy is criticized by some socionists for its lack of meaningful content. The Rational / Irrational dichotomy comes from Jung’s typology.
Static
Dynamic
|
Ne
 Ti Ti  Se Se  Fi Fi 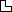 Si
 Fe Fe  Ni Ni 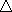 Te Te  |
Static “snapshots”, unconnected episodes
Objects and fields in constant continuous motion
|
Extroverted
Introverted
|
Ne
 Fe Fe  Se Se  Te Te  Si
 Ti Ti  Ni Ni  Fi Fi  |
Apparent qualities and causal relationships
Internal qualities, internal relationships between things
|
External
Internal
|
Si
 Ti Ti  Se Se  Te Te  Ne
 Fe Fe  Ni Ni  Fi Fi  |
Explicit, directly sensible content of reality
Implicit, indirectly perceivable content of reality
|
Irrational
Rational
|
Si
 Ne Ne  Ni Ni  Se Se  Ti
 Fe Fe  Fi Fi  Te Te  |
Perception first, unfiltered “as is” information
Judgement first, ordered evaluated information
|
Abstract
Involved
|
Ti
 Te Te  Ni Ni  Ne Ne  Fi
 Fe Fe  Si Si  Se Se  |
|
α values
γ values
|
Ti
 Fe Fe  Si Si  Ne Ne  Fi
 Te Te  Ni Ni  Se Se  |
|
β values
δ values
|
Ti
 Fe Fe  Ni Ni  Se Se  Fi
 Te Te  Si Si  Ne Ne  |
Static / Dynamic Information Elements¶
Static information is discrete and about things that change abruptly:
Ne Ne : discrete temporal phases and sets of discrete alternatives
Ti Ti : discrete logical and structural dependencies between states of affairs.
Se Se : discrete spatial boundaries that delineate territory and control.
Fi Fi : discrete types of interpersonal relationships, such as “friend” or “enemy”.
Dynamic information is continuous and about things that are in constant fluctuation:
Si Si : one’s continuous physical exchanges with one’s environment.
Fe Fe : the continuous excitations in people’s psychological states.
Ni Ni : the continuous evolution of things over time.
Te Te : the continuous incoming stream of objective facts about the world.
Extroverted / Introverted Information Elements¶
Extroverted information is information about things as they are, independent of relations to other things:
Ne Ne : something has potential or does not
Fe Fe : one is happy or sad
Se Se : one is aware of external properties of reality or not
Te Te : something is useful or not
Introverted information is information about how things relate to one another, independent of their innate properties:
Si Si : Person X is comfortable with Condition Y or is not
Ti Ti : Statement X follows logically from Statement Y or does not
Ni Ni : Course of events X will lead to Consequence Y or not
Fi Fi : Person X relates well to Person Y or does not